With the advent of Internet of Things, a connected factory is inevitable, paving the way for Industry 4.0. While many large enterprises are at the crux of Transformation it requires a calculated effort to enable this transition, starting with identifying the right solution for Machine Connectivity. The manufacturing vertical at Tech Mahindra provides dedicated IT, Engineering and consulting solutions that meet the specific requirements of OEMs and the supplier community. The unit integrates its in-depth knowledge of technology platforms, understanding of manufacturing business needs and world-class delivery capability, coupled with its partner eco-system to offer end-to-end IT and engineering solutions. In quest of providing better products with shorter innovation cycles and with high efficiency, manufacturing is becoming a constraint. The traditional factories are making ways for more flexible, more connected and more efficient manufacturing processes.
While working with various customers across different domains, TechM’s manufacturing team has seen a global trend to adapt and migrate to next level technologies. With the invent of IOT and big data analytics, more and more manufacturers are looking to enhance their manufacturing IT landscape.
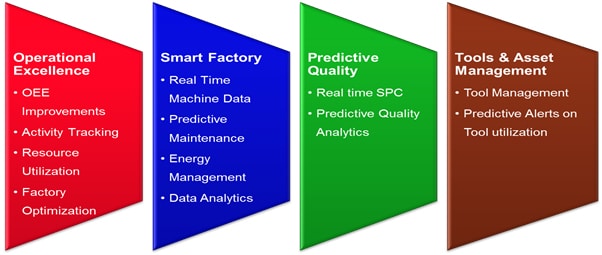
The drive is primarily to optimize Operational Excellence, to enhance Productivity and to improve Asset utilization (as given in the diagram below).
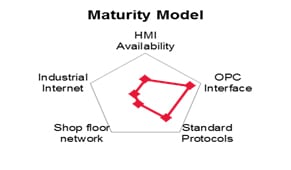
Machine connectivity is a major challenge due to the brownfield nature of the current manufacturing landscape. We at Tech Mahindra understand that the shop floor comprises – numerous different equipment which has evolved over time. In order to find the right solution, we have developed a Machine Connectivity Maturity model (MCMM) which can assess the present situation and provide a solution using IoT, IIoT, DNC, etc.
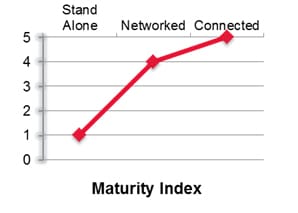
The first step in the process is to broadly categorize the machines into three major classes: Stand Alone, Networked and Connected. Industry 4.0 enables – seamless technology migration from standalone machines with, Connected machines. But before we plan the solution, it is important to understand the current status. Assessment of the current machine landscape will enable you to architect a connected environment better.
The MCMM Framework has -three main phases: Explore, Analyze and Recommend.
- Explore: The assessment team conducts workshops and discussions which would be recorded in assessment documents. The team also gathers the technical details of Machine and the IT environment.
- Analyze: Based on the recorded data, the framework will decide the score of maturity of Machine connectivity. The score is recorded for maturity as well as relevance. The final score is derived based on the scores given for individual sections.
- Recommend: The final score will be utilized to decide the solution architecture for the Machine. The existing IT environment and the Company’s IT plans are also considered along with the final score, to come out with recommended solution architecture.

MCMM: Stand Alone
The assessment scoring allows you to categorize the machines as Standalone, Networked or Connected. Any organizational objective is to achieve the highest level of maturity (Connected) to be able to find a place in Industry 4.0. Along with the classification of machines, we also emphasize on the current IT landscape, Networking landscape, and Operational Technology (OT) landscape. The analysis of the environment gives greater clarity in selecting the most appropriate solution with minimum downtime and investment.
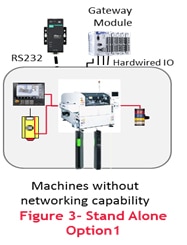
After going through the assessment process, if the assessment gives the score less than 2, the machine will be identified as Stand Alone. Typically these machines serve a special purpose or a specific operation. Most of the legacy machines also fall under this category.
Key Standalone Machine Characteristics-
- Legacy Machines/Individual Machines
- Manually operated through local control
- Work instructions, tools information locally
- Process history is either not available or available locally
- Human Machine Interface(HMI) may be available locally on the machine
- Serial RS232 connectivity may be available
Few of the integration options are as below:
- Solution Option with Gateway PLC/HW:
In this solution, Standard communication modules will be used for integration. These standard modules will be embedded in the existing architecture. The required data can be 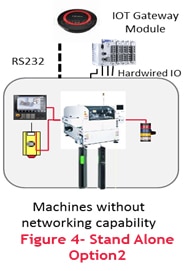 either captured from the machines. For any additional data, sensors will also be added.
either captured from the machines. For any additional data, sensors will also be added.
Advantages:
- Minimal downtime for integration
- Prevailing , Industry established hardware and software
- Additional cost for data is not required
Disadvantages:
- Changes in existing machine hardware will be required
- Changes in existing network architecture will be required.
- Less flexible in case any modifications are required.
- Solution Option with IOT Gateway:
In this solution, different IOT Gateways and IOT connectors will be used for integration. This solution will be evaluated based on the possibility of having cloud-based deployments. The required data can be either captured from the machines. For any additional data, sensors will also be integrated with IOT gateway.
Advantages:
- Minimal downtime for integration
- Use of latest technologies like IOT and Cloud
- New revenue models are available for data cost
- Higher flexibility in terms of data extraction
Disadvantages:
- Changes in existing machine hardware will be required
- New technologies might not be cost effective in short term.
MCMM: Networked
The next level of maturity is defined as “Networked”. If the assessment gives the score more than 2 and less than 4, the machine will be identified as “Networked”. These machines are typically part of Operational Technologies (OT) and are connected to plant floor networks.
Key Networked Machine Characteristics-
- Machine connected with plant floor network
- Machine parameters are available on the plant floor network
- Machine has standard industrial protocols like Profibus, Modbus, EthernetIP, Profinet
- Machines are controlled by central PLC and centralized HMI is available
- HMI has got OPC connectivity option
- Machine can be programmed to provide required parameters
Some of the integration possibilities for Networked machines are described below:
- The solution with Gateway Adapter and OPC DA:
This solution is based on leveraging existing Operational technologies and multiply the benefits of the existing landscape. The solution components are well proven and established.These solution components also provide a possibility of integrating IT with OT.
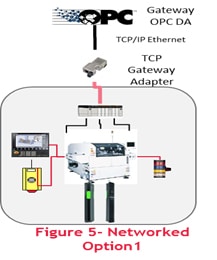
Advantages:
- Minimal downtime for integration
- Industry established hardware modules available for OPC DA
- OPC DA is established Industrial communication protocol
Disadvantages:
- Changes in existing machine hardware will be required
- Can be deployed only on Microsoft platform
- The solution with Gateway Adapter and OPC UA:
This solution is based on using secure and open architecture for OT integration. This solution will leverage the existing OT components like PLC, SCADA, and HMI to extract the information. Additional devices with OPC UA connectivity can also be integrated with this solution.
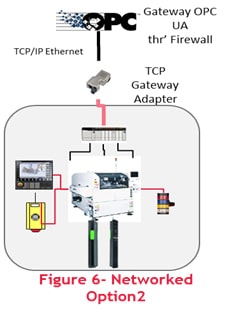
Advantages:
- Minimal downtime for integration
- Industry established gateway hardware
- Secured & Open source architecture
Disadvantages:
- Changes in existing machine hardware will be required
- Not all modules are OPC UA compliant hence another gateway might be required.
- Data acquisition rates could be slower than required.
MCMM: Connected
This is the highest level of maturity defined in the MCMM. If the assessment gives the score more than 4, the machine will be identified as “Connected”. The connected machines are easy to adapt to Industry 4.0 technologies and can be termed as Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS).
Connected Machine Characteristics-
- Machine connected with Industrial Internet
- Machine parameters are available on the Industrial Internet
- Machine has TCP based connectivity
- Machines are controlled by central PLC(Programmable Logic Controller) and centralized HMI is available
- HMI has got OPC connectivity option
- Wireless network is available for machine connectivity
- Machine can provide required parameters without any programming
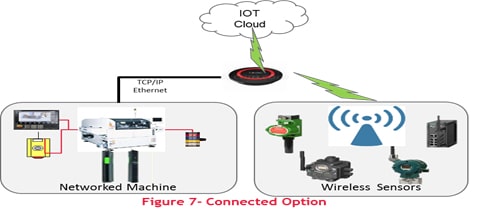
Connected machine can be integrated using IOT Gateway and Enterprise Cloud
- The solution with IOT Gateway Adapter and Enterprise Cloud:
Advanced communication modules will be used for integration with enterprise network as well as enterprise cloud.Hardware IOT gateway modules can directly communicate with IOT enabled sensors.
Advantages:
- Integration possible with new age sensors over wireless technologies.
- Industry established gateway hardware
- Minimal cable networking requirements
- Machine data is available on the Industrial internet (and also on the Internet).
Disadvantages:
- New technologies might not be cost effective in short term.
Machine connectivity is the starting point of the digital journey on the shop floor. The assessment framework provided in this White Paper provides a systematic method of understanding the current state of manufacturing IT landscape and suggesting the most suitable solutions.
The key benefits include:
- In-depth and accelerated shop floor assessment
- Optimized and rapid solution architecture definition
- Cost effective plan to define Proof of Concept (POC)
- Consultation on defining future manufacturing IT Roadmap
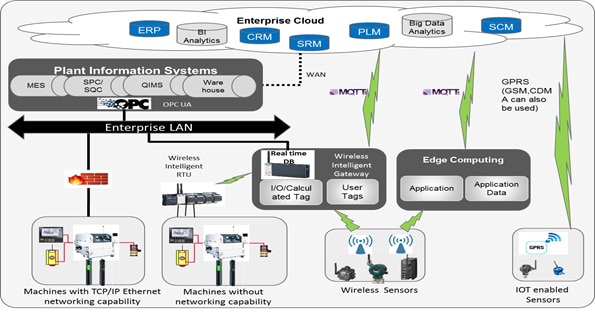
With the available technology stack, the future of the ever-evolving digital enterprise is foreseen as above (Figure1.1 State of Evolving Digital Enterprise) and MCMM Framework acts as an accelerator to move towards this future state. For any further queries or inquiries regarding this white paper, please write to ( Sales@TechMahindra.com)
About the Author:
About the author:
Kedar Sahasrabudhe joined Tech Mahindra with more than 17 years of Manufacturing, IT and Control Systems experience. He gathered domain knowledge while working for Global Automation companies like Siemens and Rockwell Automation. After gaining extensive manufacturing IT experience, Kedar contributed to IT consulting organizations like Accenture and Tata Consultancy Services to architect effective, robust and innovative solutions.
Kedar has been working on various IT platforms based on Siemens, Allen Bradley as well as SAP to deliver solutions to discrete and process manufacturers spread across the globe. He was instrumental in delivering the first ever manufacturing execution system implementation among Indian Automotive OEMs. He also played a key architect role in transformational deliveries across the globe in Manufacturing Operations Management (MOM), Machine Connectivity and Industrial Automation.
At Tech Mahindra, Kedar is leading all the initiatives related with the Factory of Future in discrete as well as process industries.
Kedar holds a Bachelor’s Degree in Electronics Engineering from Walchand College of Engineering, India and a Post Graduate Diploma in Operations Management from ICFAI, India.





useful but techy